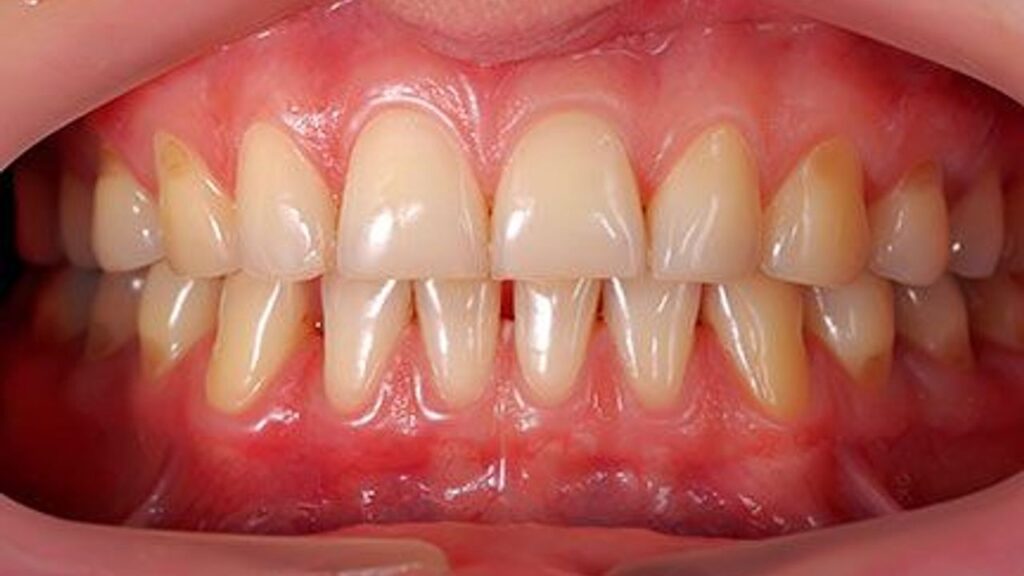
Gingival recession pertains to the shrinking of the gum line down the tooth or the wearing away of the gum line with a part of the tooth or the root is exposed. This situation causes heightened sensitivity, higher susceptibility to caries and even aesthetic problems. Knowledge of the conditions contributing to oral health and oral diseases and their signs as well as the approaches, which are taken in order to eradicate them are very essential.
Causes of Receding Gums
Several factors contribute to gum recession:Several factors contribute to gum recession:
- Periodontal Diseases: Gum diseases which are caused by bacteria and lead to loss of gum tissue and bones supporting the teeth are another cause of recession.
Genetics: Gum disease is a problem that certain people may not be able to avoid even if they practice excellent hygiene.
Aggressive Brushing: Brushing your teeth in significantly hard motion or using a hard bristle of the brush can lead to the wearing off of the enamel and the retraction of the gums.
Poor Dental Care: Frequent poor brushing, flossing, and rinsing can lead to the formation of tartar, a hard substance from the plaque which leads to gum retraction.
Hormonal Changes: Puberty, pregnancy, and delivery, or menopausal changes in hormonal balance also exert influence on gum tissues and render them more sensitive and susceptible to recession.
Tobacco Use: Smoke or chew tobacco because it leads to the damage of gum tissues, and hence results in the retraction of gums.
Grinding and Clenching Teeth: These actions can place a high pressure on the teeth; this leads to a particular degree of retraction of the gum line.
Misaligned Teeth: Misalignment of the teeth adversely affects the gum and bones on which the teeth are located, and this leads to development of recession.
Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of receding gums early can help in managing the condition effectively:Recognizing the symptoms of receding gums early can help in managing the condition effectively:
- Visible Lengthening of Teeth: It may look like your teeth are longer than they are,” the synopsis notes.
Increased Sensitivity: Gum recession results in the exposure of the tooth surface and it may cause discomfort upon consuming hot or cold food items and beverages, or even sweetness and acidity.
Notch Near the Gum Line: Generalised patterns included, a slight ridge at the level of the gum line or a noticeable notch or groove at the same level.
Gum Inflammation and Redness: Gingival enlargement, specific lip color change, or the presence of bloody saliva following brushing or flossing.
Loose Teeth: In severe cases, the gums may recede further and pull the teeth out or at least cause the person to lose them.
Treatment Options
Treatment for receding gums depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition:
- Improved Oral Hygiene: Brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using proper technique, and regular flossing can prevent further recession.
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning method that removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smooths the root surfaces.
- Antibiotics: Medications to eliminate remaining harmful bacteria.
Surgical Options:
- Gum Grafting: Tissue from the roof of the mouth or another source is used to cover exposed roots.
Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST): A minimally invasive procedure that involves making small holes in the gum tissue to loosen and reposition it over the receded areas.
Regeneration: Procedures using membranes, graft tissues, or proteins to stimulate tissue and bone regrowth in severe cases.
Prevention
Preventing gum recession involves adopting good oral hygiene practices and making lifestyle changes:
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Routine visits to your dentist in Lahore for professional cleanings and examinations.
Proper Brushing and Flossing: Using a gentle technique and soft-bristled brush.
Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals that support gum health.
Avoid Tobacco Products: Refraining from smoking or chewing tobacco.
Stress Management: Reducing stress to avoid teeth grinding and clenching.
Conclusion
Receding gums can significantly impact oral health and aesthetics. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatments, individuals can take proactive steps to manage and prevent this condition. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene are fundamental in maintaining healthy gums and preventing recession. For the treatment of receding gums refer to a dentist in Karachi.